47: Creating and modifying HTML
11th October 2012: Material moved to webplatform.org
The Opera web standards curriculum has now been moved to the docs section of the W3C webplatform.org site. Go there to find updated versions of these docs, and much more besides!
12th April 2012: This article is obsolete
The web standards curriculum has been donated to the W3C web education community group, to become part of a much bigger educational resource. It is constantly being updated so that it remains current with modern web design practices and technologies. To find the most up-to-date web standards curriculum, visit the web education community group Wiki. Please make changes to this Wiki yourself, or suggest changes to Chris Mills, who is also the chair of the web education community group.
- Previous article—Traversing the DOM
- Next article—Dynamic style - manipulating CSS with JavaScript
- Table of contents
Introduction
In this article I’ll explain the basics of using JavaScript to manipulate the content of your pages, including showing and hiding parts of a page, and adding new HTML and removing it. At the end of this you’ll understand that the most fundamental thing we use JavaScript for is to change the contents of pages, and you’ll understand the best ways to do this.
The article contents are as follows:
Hiding and showing
The easiest place to start is with manipulating the HTML you’ve already
got, by hiding or showing elements that are already in the page. To do this,
you can use JavaScript to change the styles on an element. CSS styles are already a
powerful way of describing how an element looks, and one part of how an
element looks is whether it’s displayed at all. The CSS display
property is the key to showing and hiding an element: setting it to
display:none; hides an element. Imagine a paragraph like this:
<p id="mypara" style="display: none">I am a paragraph</p>That paragraph would be invisible on the page. JavaScript allows you to
dynamically add that display: none style to that element
and take it away.
JavaScript is designed to allow you to get a reference to an HTML
element. For example, var el = document.getElementById("nav"); will
give you a reference to the element with id="nav". Once you’ve got
a reference to an element, you can change the CSS applied to it by using the style attribute. For example, our above
“mypara” paragraph is currently hidden (it has display: none set).
To show it, set the style attribute display to
block:
var el = document.getElementById('mypara');
el.style.display = 'block';And lo, the paragraph appears. Setting CSS on an element through the
style attribute does the same thing as setting it in the
style attribute in the HTML itself, so the above code setting
el.style.display = 'block' achieves the same effect as putting
style="display: block" directly in your HTML. Except that it’s dynamic. Hiding any element is just as simple:
var el = document.getElementById('mypara');
el.style.display = 'none';Hiding and showing example
Theory is all good, but a more practical example may be useful here. Imagine a set of tabs, where clicking on the tab itself shows it and hides all the others.
Here’s an example of a set of tabs:
<ol class="tablinks">
<li><a href="#tab1">Tab 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab2">Tab 2</a></li>
<li><a href="#tab3">Tab 3</a></li>
</ol>
<div class="tab" id="tab1">This is tab 1</div>
<div class="tab" id="tab2">This is tab 2</div>
<div class="tab" id="tab3">This is tab 3</div>In the head of the example file (see tabs.html for the live example), you’ll find the following CSS and JavaScript (these would normally be put in external files and imported into the HTML, but I’m keeping everything in one file here to make things simpler to navigate). Some of the code looks intimidating; don’t worry, we’ll go through it.
<style type="text/css">
ol.tablinks {
margin: 0; padding: 0;
}
ol.tablinks li {
float: left;
border: 2px solid red;
border-width: 2px 2px 0 2px;
background: #eee;
list-style: none;
padding: 5px;
margin: 0;
}
ol.tablinks li a {
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
}
div.tab {
clear: left;
border: 2px solid red;
border-width: 1px 2px 2px 2px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
var tabify = {
hasClass: function(el,c) {
return el.className.match(new RegExp('(\\s|^)'+c+'(\\s|$)'));
},
addClass: function(el,c) {
if (!tabify.hasClass(el,c)) el.className += " " + c;
},
removeClass: function(el,c) {
if (tabify.hasClass(el,c)) {
el.className=el.className.replace(new RegExp('(\\s|^)'+c+'(\\s|$)'),' ');
}
},
hideAllTabs: function(ol) {
var links = ol.getElementsByTagName("a");
for (var i=0; i<links.length; i++) {
tabify.setTabFromLink(links[i], "none");
}
},
setTabFromLink: function(link, style) {
var dest = link.href.match(/#(.*)$/)[1];
document.getElementById(dest).style.display = style;
if (style == "none") {
tabify.removeClass(link, "active");
} else {
tabify.addClass(link, "active");
}
},
addEvent: function(obj, type, fn) {
if ( obj.attachEvent ) {
obj['e'+type+fn] = fn;
obj[type+fn] = function(){obj['e'+type+fn]( window.event );};
obj.attachEvent('on'+type, obj[type+fn] );
} else {
obj.addEventListener( type, fn, false );
}
},
init: function() {
var ols = document.getElementsByTagName("ol");
for (var i=0; i<ols.length; i++) {
var ol = ols[i];
if (!/(^|\s)tablinks(\s|$)/.test(ol.className)) { continue; }
tabify.addEvent(ol, "click", function(e) {
var target = window.event ? window.event.srcElement : e.target;
if (target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === "a") {
tabify.hideAllTabs(e.target.parentNode.parentNode);
tabify.setTabFromLink(e.target, "block");
if (e) e.preventDefault();
if (window.event) window.event.returnValue = false;
return false;
}
}, true);
tabify.hideAllTabs(ol);
tabify.setTabFromLink(ol.getElementsByTagName("a")[0], "block");
}
}
};
tabify.addEvent(window, "load", tabify.init);
</script>Each tab is a link. Each link has an onclick
event handler on it. That event handler does
two things: it hides all the divs (using the
display: none approach from above) and then shows
the div corresponding to that tab, by setting that
div’s style to display: block.
You’ll have noted that the HTML here is set up to still make sense even in the absence of scripting; while clicking a link won’t show or hide a tab, the links jump to the appropriate tab, so the page still operates correctly and makes semantic sense even in a browser without JavaScript. This is important: it’s a technique that you may have heard referred to as “progressive enhancement” (or, in the ancient tongue of three years ago “graceful degradation”, but we don’t call it that any more). It’s important not only for people who are using some modern browser but with JavaScript turned off, but for a host of other user types as well. Assistive technologies such as screen-readers for blind users rely heavily on the structure of your HTML being semantic and meaningful, and their support for JavaScript enhancements is not as good as those for sighted users. Mobile browsers also tend not to have as much useful support for scripting. Search engines also read your HTML and not your script—it could be said that Google is the world’s most voracious blind browser user. This is the meaning of the term “progressive enhancement”: start with a page that makes sense and displays its content in the most simple of environments, such as a text-only web browser, and then gradually add extra functionality to it so that at every step of the way your site is still usable and functional.
All JavaScript code basically comes in two parts: the part that actually does the work, and the part that hooks up that bit to the HTML. The code that actually does the work in this example is pretty trivial: showing the corresponding tab to a particular link is two lines of JavaScript:
var dest = link.href.match(/#(.*)$/)[1];
document.getElementById(dest).style.display = "block";The links, if you remember, look like <a href="#tab1">Tab 1</a>
and so the first line uses a regular expression (see the note below) to extract
the part of the link that appears after the # symbol; in this
example that would be the string tab1. That part of the link is the same as
the ID of the corresponding div (because, as mentioned, the page
is built to make sense semantically, so a “tab” links to its div).
We then fetch a reference to that div with
document.getElementById, and set style.display to
block as previously discussed.
Regular expressions
Regular expressions are a sort of mini-programming-language designed to help with the problem of “parsing” text—for example, answering questions like “does this string appear inside this other string?“ and “in the string ‘abc123def’, what are the numbers between ‘c’ and ‘d’?” They’re a very powerful tool, but they’re also pretty complicated. There’s a description below of what the regular expression is for; for now, though, feel free to take how they work on trust and come back to it later.
The “regex” (short for “regular expression”) used in this example is
/#(.*)$/. Each character in a regular expression is designed to
match against a sequence of characters in some target string; the idea is
to express how a target string is made up, in sections.
/ … /— the slashes denote the start and end of a regex, just like double or single quotes do for a “string”#— the hash symbol (#) actually means “match a hash symbol”( … )— brackets mean “here is a section of the string that I’ll be interested in later”.*— this means “any characters you like”; it’s actually a dot (.), meaning “any one character”, followed by asterisk (*) meaning “repeat as many times as you want”$— the dollar means “the end of the string”
So our regex describes a “matching pattern” for a string comprised of “a hash,
followed by whatever characters you want”. link.href is the
destination of the link we’re looking at (for example, #tab1, and
since this is a string described by “a hash followed by whatever
characters you want”), the “matching pattern” does apply to this
string.
link.href.match(our_regexp), therefore, will return
a true rather than false result; what it actually returns is an array of two
things, ["#tab1", "tab1"]. The first is the text that was matched
by the whole regex, and the second is the text matched inside the brackets; this
is why the brackets are there—to mark that part of the string as “this is the
bit we care about”. That tab1 is the string we want, so we can
grab it out of the returned array (it’s the second item, so [1]
will grab it — arrays start numbering at zero.)
Connecting the working code to the page
As mentioned above, there are two parts to the code: the part which actually
does the work, and the part which hooks up that bit to the HTML. Hooking up the
working code to the HTML is what events are for. In this particular example,
we care about two events: the window’s load event,
which is used to say “start everything off”, and the tab list’s
click event, which is fired when the user clicks on a tab. When the
page loads, we need to run the connection code, and the connection code should
connect the tab click event to the code above, which displays the
appropriate tab.
Running code in response to an event is done with the
addEventListener function in most browsers and with the
attachEvent function in Internet Explorer. Here we are creating a “wrapper” function, which does the right thing depending on which is supported:
addEvent: function(obj, type, fn) {
if ( obj.attachEvent ) {
obj['e'+type+fn] = fn;
obj[type+fn] = function(){obj['e'+type+fn]( window.event );};
obj.attachEvent('on'+type, obj[type+fn] );
} else {
obj.addEventListener( type, fn, false );
}
}(Don’t worry too much about how this works; just take it on trust for now—you’ll understand it better as you become more experienced in JavaScript.)
This function takes three parameters, obj, type,
and fn, which are “the object that fires the event”, “the
event we care about”, and “the function to run when the event fires”.
We need to run our function called tabify.init when the page loads;
the tabify.init function will then take care of hooking up each
tab’s click event.
addEvent(window, "load", tabify.init);As you can see from the HTML structure above, a set of tabs are actually
expressed as an ordered list with class="tablinks". So the
tabify.init function needs to do the following:
- Find all the
<ol>s on the page with a class oftablinks - Attach to each
<ol>’sclickevent some code that does the following:- Work out exactly which tab link the user clicked on
- Work out which actual tab corresponds to that tab link
- Show that one tab
- Hide any other tabs
The init function that does all this looks like so:
init: function() {
var ols = document.getElementsByTagName("ol");
for (var i=0; i<ols.length; i++) {
var ol = ols[i];
if (!/(^|\s)tablinks(\s|$)/.test(ol.className)) { continue; }
tabify.addEvent(ol, "click", function(e) {
var target = window.event ? window.event.srcElement : e.target;
if (target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === "a") {
tabify.hideAllTabs(e.target.parentNode.parentNode);
tabify.setTabFromLink(e.target, "block");
if (e) e.preventDefault();
if (window.event) window.event.returnValue = false;
return false;
}
}, true);
tabify.hideAllTabs(ol);
tabify.setTabFromLink(ol.getElementsByTagName("a")[0], "block");
}
}Let’s walk through this function step by step, looking at what each part does in turn:
var ols = document.getElementsByTagName("ol");
for (var i=0; i<ols.length; i++) {
var ol = ols[i];
if (!/(^|\s)tablinks(\s|$)/.test(ol.className)) { continue; }
}This finds all the <ol>s on the page with a class of tablinks—it then pulls up a list of all <ol>s and for each one,
says “if this doesn’t have a class of ‘tablinks’, then skip it”.
(Checking the class is done with a regular expression; continue
means “skip over this one and on to the next”.)
tabify.addEvent(ol, "click", function(e) {
...
});This attaches some code to each <ol>’s click event.
var target = window.event ? window.event.srcElement : e.target;This works out exactly which tab link the user clicked on…
tabify.setTabFromLink(e.target, "block");…then this shows that single tab…
tabify.hideAllTabs(e.target.parentNode.parentNode);…and finally, this line hides any other tabs.
The setTabFromLink and hideAllTabs functions are
also in the code; they use the techniques above to hide a tab or show it.
Take a look at them to see how they work — they’re separate functions
because it’s often useful to take a block of code that’s called from more
than one place and put it in its own function. (It makes your code easier
to understand and reuse in multiple places. People will sometimes refer to this as “breaking out” or “factorising” code into a function.)
There's a bit of "extra credit" work in there as well, which neatly
demonstrates more adding and removing of attributes. The setTabFromLink
function not only displays the appropriate tab but also sets
class="active" on the "active" tab. It does this with the help
of three utility functions, hasClass, removeClass, and
addClass. In the same way that we hide all the tabs and then show
the active one, we use removeClass to remove "active" from the
className of all the tablinks and then addClass to add
"active" to the one tablink which is actually active. Just adding a class to
a link may seem pointless — after all, classes are invisible — but
it's a hook for styling. We can (and have) make links with
class="active" appear differently, by adding extra CSS:
ol.tablinks li a {
background-color: red;
}
ol.tablinks li a.active {
background-color: white;
}So now, the "active" tab appears in white, while other tabs appear in red. Using JavaScript to add and remove classes is a very common technique, and one that you should use whenever possible; CSS is good at controlling layout and position and appearance of your HTML elements, and so using JavaScript to alter the classes on those elements means that they can pick up different CSS styles. It's an ideal unification; JavaScript makes your elements dynamic but doesn't actually change very much itself. Just add a class and let CSS do the heavy lifting.
Creating HTML
DOM scripting is much more powerful than simply altering the CSS properties of your existing HTML, though. You can also dynamically create new HTML that was never in your page to begin with. For example, on the tech news site Slashdot, a link in a comment displays the destination of the link in square brackets, so a link like <a href="http://opera.com">A web browser</a> will display as <a href="http://opera.com">A web browser</a> [opera.com]. (They did this to stop people being rickrolled, or worse.) Adding this extra bit of HTML, displaying the destination domain of every link on the page, will be easy to do with JavaScript.
Creating new HTML elements is done with the
document.createElement function. For this
example, we only need to add one thing: after each link, we’ll add a
span containing text listing the domain of the link (check out linkify.html for a live example). The HTML for the example looks like this:
<p id="start">This is some text that has
<a href="http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/struct/links.html">links</a> in it
to various places, including <a href="http://www.opera.com">Opera</a>,
<a href="http://www.bbc.co.uk/">the BBC</a> and an internal link to
<a href="#start">the beginning of this section</a>. All the external links
should have <span>[domain]</span> after them.</p>The JavaScript looks like this:
<script type="text/javascript">
var linksuffix = {
addEvent: function(obj, type, fn) {
if ( obj.attachEvent ) {
obj['e'+type+fn] = fn;
obj[type+fn] = function(){obj['e'+type+fn]( window.event );};
obj.attachEvent('on'+type, obj[type+fn] );
} else {
obj.addEventListener( type, fn, false );
}
},
init: function() {
var links = document.getElementById("linksuffixtext").getElementsByTagName("a");
for (var i=0; i<links.length; i++) {
var matches = links[i].href.match(/^http:\/\/(.*?)\//);
if (matches) {
var linkdomain = matches[1];
var span = document.createElement("span");
var spantext = document.createTextNode(" ["+linkdomain+"]");
span.appendChild(spantext);
links[i].parentNode.insertBefore(span, links[i].nextSibling);
}
}
}
};
linksuffix.addEvent(window, "load", linksuffix.init);
</script>The part of the script that does the work here is as follows:
var links = document.getElementsByTagName("a");
for (var i=0; i<links.length; i++) {
var matches = links[i].href.match(/^http:\/\/(.*?)\//);
if (matches) {
var linkdomain = matches[1];
var span = document.createElement("span");
var spantext = document.createTextNode(" ["+linkdomain+"]");
span.appendChild(spantext);
links[i].parentNode.insertBefore(span, links[i].nextSibling);
}
}This breaks down like this:
var links = document.getElementsByTagName("a");
for (var i=0; i<links.length; i++) {
...
}
First, it finds all the links (getElementsByTagName("a")) in the document
var matches = links[i].href.match(/^http:\/\/(.*?)\//);
if (matches) {
...
}
This line uses a regular expression on each link to find out whether the destination of the
link begins with http://something/. If it does…
var linkdomain = matches[1];
var span = document.createElement("span");
var spantext = document.createTextNode(" ["+linkdomain+"]");
span.appendChild(spantext);…this next part first gets the “linkdomain”, the www.opera.com part of the link. It next creates a <span> element using
document.createElement. Next, it creates a “textNode”. While HTML
elements themselves are created with document.createElement,
all text in an HTML document is actually contained within
“textNode”s, and you have to create those separately. You
don’t have to worry about this (or even know about it) when writing
actual HTML, but you do have to know about it when creating elements using
DOM scripting. The text in the textNode is actually “ [domain]”,
created by concatenating (adding together)
strings. Finally, this part uses the <span>’s
appendChild method to put the textNode inside the span.
links[i].parentNode.insertBefore(span, links[i].nextSibling);
This line adds the span into the document. At this point, span is a reference to an HTML
element that looks like this:
<span> [example.com]</span>That element however isn’t part of the document. It’s not part of any document yet; it’s just floating around in limbo. Adding the element to the document can be
done in one of two ways: using appendChild as above, or using
insertBefore. The appendChild function adds our new
element at the end of an existing element (that’s why it’s called
append). Since we want to add it in the middle of an existing element,
we need insertBefore. Remember that our current bit of HTML looks
something like this:
<p>... text that has
<a href="http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/struct/links.html">links</a> in it
to ...This equates to a DOM tree looking something like Figure 1:
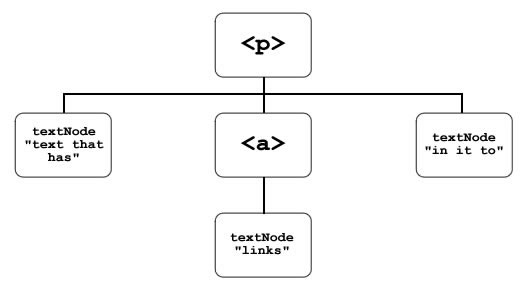
Figure 1: The DOM tree before the addition of the span element after the link
We want to insert our new span in between the <a> and the
“in it to” textNode, so that it appears after the <a>. This would leave our DOM tree looking like Figure 2:
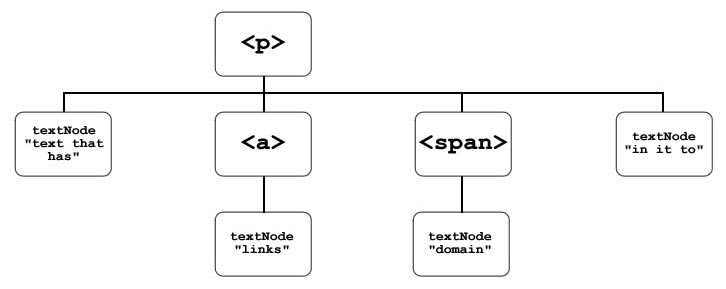
Figure 2: The DOM tree after the addition of the span element
or, more simply, HTML such as
<p>... text which has
<a href="http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/struct/links.html">links</a>
<span> [domain]</span> in it to ...What would be handy here is to be able to say “insert our new
span after the link”. Sadly, there is no
insertAfter function. Instead, we need to insert it
before the thing after the link (confusing, but think about it and
it’ll make sense). A quick shortcut to “the thing after an element labelled
el” is el.nextSibling. The insertBefore
function needs to be called on the element that you’re inserting into, which
is the parent <p> of the link, quickly accessible with
link.parentNode. So the full call, as above, is
links[i].parentNode.insertBefore(span, links[i].nextSibling);
That is, find the parent (<p>) of the link we’re currently
processing (links[i]), and insert our created span element
(span) before the thing after the link
(links[i].nextSibling). Treating HTML as a DOM tree in this way
and inserting new elements into it can be confusing at first, but it soon
becomes clearer as you get more practice at it.
Summary
HTML provides the structure of your pages, and CSS provides the description of how it looks. What JavaScript brings is flexibility; your HTML structure and your CSS styles become dynamic. You can change how your pages look and feel and work from moment to moment, based on what your users do. It’s the next step up: from well-thought-out and well-structured information to data that changes depending on what your users need. You can show and hide elements, change styles and appearances, and add new HTML or remove the old in whatever way you need to.
Exercise questions
- How do you set an element’s CSS display property to hide an element?
- What’s the difference between an element and a text node?
- Give two reasons why progressive enhancement is important.
- What’s the difference between
appendChildandinsertBefore? - Why do we use an
addClassfunction rather than just concatenating the new class name with an existing element'sclassNameattribute? In the following HTML structure, what would
document.getElementById("marker").nextSiblingbe?<p>This is a <strong>block of HTML with <span id="marker">various markup<span> in it</strong>.</p>
- Previous article—Traversing the DOM
- Next article—Dynamic style - manipulating CSS with JavaScript
- Table of contents
About the author

Stuart Langridge is quite possibly the only person in the world to have a BSc in Computer Science and Philosophy. When he's not fiddling about with computers, he's a JavaScript, Django, and Python hacker at Canonical, author of SitePoint's DHTML Utopia, and a drinker of decent beers. He's also one-quarter of the team at LugRadio, the world's premiere Free and Open Source Software radio show. His ramblings about the web, scripting, open source software, and whatever else floats past the window are to be found at kryogenix.org; Stuart is to be found outside looking for the smoking area.
liThis article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution, Non Commercial - Share Alike 2.5 license.
Comments
The forum archive of this article is still available on My Opera.
No new comments accepted.